Enzymes
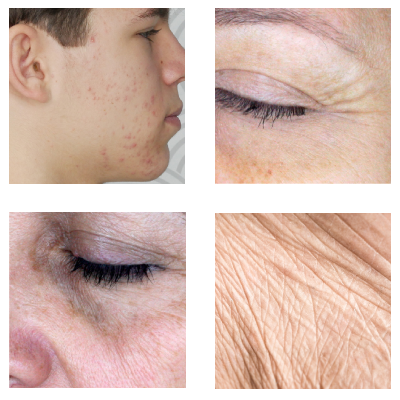
Enzymes are vital substances for cells, they are biocatalysts that increase the reaction rate of processes occurring in the body. Since every enzyme is a protein, their function is strongly influenced by temperature and PH. Each has an optimal temperature and PH value. Higher temperature increases the reaction rate, but if it is too high, the enzyme denatures. Each enzyme is specific: it can only catalyze the reaction of a particular compound or group of compounds, so one enzyme can't replace another. Enzymes - but not necessarily the same enzymes - simultaneously perform destructive and constructive tasks. On the one hand, they participate in the breakdown of fats, proteins and carbohydrates (i.e., in the process of digestion), on the other hand, they assist in the operation of the immune system in various ways and in various places by destroying and damaging pathogens and their toxins: on the skin surface, at body openings (saliva, tears, airways), and even within the body. We also make use of enzymes at home: we remove contaminants and stains with the help of the fat and carbohydrate breaking enzymes of washing and dishwashing detergents. We clean contact lenses with a solution containing enzymes to remove proteins that can cause infection. They are also used in the pharmaceutical industry, for example, in the production of certain antibiotics, and in the food industry (in the production of bakery and dairy products), they are downright indispensable. In our diet, they play an extremely important role not only in breaking down, but also in releasing essential vitamins, amino acids and minerals. The physiological significance of many vitamins lies precisely in their ability to enable normal cell function as parts of coenzymes. Such are nicotinamide, riboflavin (B2 vitamin), biotin, pantothenic acid, thiamine (B1 vitamin), folic acid, or B12 vitamin. Their natural sources are raw vegetables, eggs, not overly processed meat and fish. Due to the extremely large number and function of enzymes, cosmetics can utilize them in many different ways.
FAQs From Same Category
Natural acids called fruit acids, which are not exclusively produced in fruits (e.g. apples, citrus fruits, quinces, grapes…) but also in milk and sugarcane. In addition to hydrating, their most well-known property is the so-called peeling effect, that is, they stimulate the natural process of peeling, which can be disturbed due to skin aging and damage caused by sunlight. Alpha hydroxy acids (and especially glycolic acids) are indispensable for ensuring smooth and fresh facial skin, not only because they are effective against keratinization and play a major role in the removal of dead skin cells, but also because they stimulate the formation of collagen responsible for skin elasticity and beauty, and they also have spot-reducing properties by speeding up the fading of the pigment substance, the so-called melanin dye cell, formed by the sun. In summary: alpha hydroxy acids increase blood flow, stimulate circulation, reduce wrinkles, dissolve surface keratin and improve the skin's water-binding - that is, moisturizing - ability. Their exfoliating and skin renewing effect appears almost within days, but the complete renewal of the skin takes place over a 28-day cycle. During this time, the skin "renews", the process of keratin formation takes place, the skin regenerates. Although under different names, the use of AHA acids goes way back. Cleopatra bathed in sour donkey milk, the ladies of the Sun King's court washed with grape juice, and in the old Hungarian villages, the bride received a grated apple mask so that she would be led to the altar with a velvety and fresh face the next day. Nowadays there are very effective, concentrated AHA- creams, which, however, due to the strong peeling effect making the skin thinner and more sensitive, it is advisable to consult with a beautician or dermatologist. These exfoliating creams should never be used around our eyes. It is also worth paying attention to whether the alpha hydroxy acid in our skincare product is of natural origin. Because there are synthetic products as well, and it is not at all the same which one we use. The Armonía snail products (both the Genuine and the Armonía natural brand Helix Aspersa product lines) contain alpha hydroxy acids in a ratio that fully ensures the skin regenerating effect, but cannot cause the itching or skin redness that sometimes occurs with AHA treatments.
The vitamin known mainly as biotin belongs to the family of B vitamins and, as such, is soluble in water. Biotin is the protective vitamin of the epithelial tissue, an important enzyme of bacteria and yeasts. Similar to B vitamins, it participates in the breakdown of fats, proteins, and carbohydrates, aids in the utilization of proteins, folic acid, pantothenic acid, and B12, and plays an important role in the production of essential fatty acids for the skin and hair. It is highly valued in cosmetics because it ensures healthy skin, hair, and nails, but it is also indispensable for the eyes and liver. It can improve the condition of eczema and skin inflammations and increases the insulin sensitivity of cells, which can be useful for diabetics. Its deficiency reduces the resistance of the epithelial tissue, the skin dries out, becomes scaly, in more severe cases inflammations can occur, hair loss can occur, it can reduce sexual desire, and can even cause spinal cord problems. Regular alcohol consumption makes it difficult to absorb biotin, while smoking requires a larger intake.
Its natural sources are liver, kidney, egg yolk, yeast, sardines, cottage cheese, cauliflower, spinach, banana, hazelnuts, almonds, walnuts, sesame seeds, beans, soybeans, cereals, unpolished rice, mushrooms. Few H-vitamins can be found in fruits and meats.
A natural polysaccharide that can be found in all tissues. In the human body, among other things, it has a water-binding role and lubricates the joints and muscles. 56% of the hyaluronic acid in the human body is found in the connective tissues of the skin, 35% in the muscles and bones, and the remaining 9% in the synovial fluid, blood and lymph. As age progresses, the quantity of hyaluronic acid decreases in the body, leading to a reduction in the volume of the connective tissue, thereby leading to a deterioration in skin tone and deepening wrinkles. Its consistency and tissue-friendly nature make it suitable for inclusion in numerous pharmaceutical products, particularly in ophthalmic and osteoarthritis-related products. Thanks to its special water-binding ability - a single molecule can retain 1000 water molecules - it is used very effectively in cosmetics to fill wrinkles, lift sagging neck skin, tighten décolletage, and even for lip augmentation. Hyaluronic acid can be obtained from tissues with a high hyaluron content (e.g. rooster comb), or it can be produced by bacterial fermentation. It is a common component of moisturizing, wrinkle-smoothing creams, but due to its high production cost, it is usually only present in negligible amounts.
Vital organic compounds, which have both an amino group and a carboxyl group in their molecule. They are the building blocks of protein molecules, so the body's protein requirement also means an amino acid requirement. There are 25 types of amino acids in the body, of which 20 are protein building. Those amino acids that the body cannot or can only partially produce are called essential. For the human body, 9 amino acids are essential: methionine, threonine, lysine, isoleucine, valine, leucine, phenylalanine, tryptophan, and histidine. The biological value of proteins is determined by their essential amino acid content. The so-called primary or complete proteins contain all essential amino acids in adequate quantities and are therefore sufficient as the sole source of protein. Animal proteins belong to this group, such as meat, fish, milk, eggs ... secondary or incomplete proteins lack certain essential amino acids, therefore they are not sufficient as protein sources on their own, but can be made complete by combining them with another incomplete or complete protein. Plant proteins belong to this group.